Table of Contents
- Do Probiotics help with Yeast Infections?
- Can Probiotics cause a Yeast infection?
- Can you use Probiotics in Yogurt for the treatment of a Yeast Infection?
- What are some good Probiotics for the treatment of Yeast infections?
- What are the benefits of Yeast based Probiotics?
- What are the benefits of Probiotics for the treatment of Yeast overgrowth?
- Is inserting Probiotics for Yeast infection safe?
- Are Probiotics with Acidophilus strains useful for treating a Yeast infection?
- Is taking Probiotics with Antibiotics effective to prevent a Yeast infection?
- What is the relationship between Probiotics and Yeast allergy?
- How long does it take for Probiotics to work for Yeast infection?
- What is the dosage of Probiotics for Yeast infection?
- Can Probiotics cause Yeast to die off?
- Want to know more?
- Sources
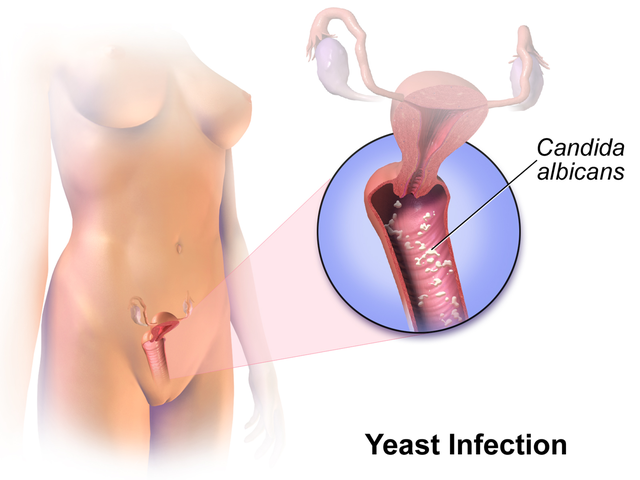
Do Probiotics help with Yeast Infections?
Certain probiotics such as Lactobacilli can help with yeast infections because they can kill the Candida yeast. Most yeast infections are caused due to Candida albicans. Studies show that probiotics exert a fungicidal activity, which helps decrease or remove various strains of candida.
A study performed in the laboratory evaluated the effectiveness of lactobacilli against candida for the treatment of yeast infections. The study showed that strains of lactobacilli inhibited the growth of candida. The inhibitory action was attributed to the activity of organic acids. The study also demonstrated the in-vivo effectivity of probiotics in yeast infections by assessing vaginal washes.
Can Probiotics cause a Yeast infection?
Yeast-based probiotics (such as the Saccharomyces boulardii strain) can cause a yeast infection if consumed by patients who are prone to it. Upon consumption, yeast can enter the bloodstream and may cause a condition known as bacteremia. Several case reports of probiotics causing the condition have been reported.
However, in a normal adult, the probiotic does not cause infection but protects from it. The probiotic increases the number of good bacteria especially Lactobacilli which helps combat the fungal infections caused due to yeast. Probiotics in different forms such as oral or vaginal are used to treat or prevent yeast infections.
In the video below, Dr. Bentley explains how probiotics can be beneficial for yeast infections and UTIs:
This is our recommended Probiotic Supplement for Yeast Infections:

Gut+ from ProBiology (Probiotics + Prebiotics Formula)
Can you use Probiotics in Yogurt for the treatment of a Yeast Infection?
Probiotics in yogurt can be used to treat a yeast infection because the lactobacilli in the yogurt inhibit yeast growth. Probiotic yogurt is a rich source of various beneficial bacteria including lactobacilli, bifidobacterium, and their different strains.
A study was conducted on 129 pregnant women, in which the women used a mixture of honey and yogurt vaginally to treat yeast infection, and the other group used a usual antifungal agent. The research found that the mixture had a high cure rate and can be used as an alternative treatment to treat yeast infections.
In another study non-pregnant women applied the mixture of honey and yogurt vaginally. The other group of participants like in the previously mentioned study used a standard anti-fungal treatment. The researcher reported that the mixture containing yogurt reduced the symptoms of yeast infection and therefore can be used as a herbal remedy.
What are some good Probiotics for the treatment of Yeast infections?
The following are some good probiotics for the treatment of yeast infections:
- Lactobacillus acidophilus: It is a strain of lactobacilli and several studies show its effectiveness in treating yeast infections. The lactobacilli possess the ability to kill candida and prevent infection. The probiotic also has the ability to remove candida from the GI tract and reduce the symptoms of the infection.
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus: It protects against vaginal infections by interfering with the growth and development of candida, and the adhesion of yeast to the vaginal epithelial wall.
- Bifidobacterium: This probiotic is also useful for the treatment of yeast infections, it is also used to prevent candida infection in patients undergoing chemotherapy. A product containing bifidobacterium has been patented to treat yeast infections.
What are the benefits of Yeast based Probiotics?
Saccharomyces boulardii is a yeast-based probiotic used for the prevention and treatment of diarrhea along with various GI disorders. S. boulardii inhibits the growth of numerous microbes, passes through the GI tract unharmed, and has an optimum temperature of 370 C making it a potential probiotic.
The following are some benefits of yeast-based probiotics:
- Decreases symptoms of SIBO: The probiotic yeast Saccharomyces Boulardii improves the outcomes of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth when used along with regular treatment.
- Decreases constipation: Yeast-based probiotics can help decrease constipation.
- Helps with leaky gut syndrome: S. Boulardii, a yeast-based probiotic, restores the function of the intestinal barrier decreasing the permeability of the intestinal wall, thus helping to reduce symptoms of the leaky gut syndrome.
- In treating IBS: Yeast-based probiotics improve the symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Studies show that the consumption of S. Boulardii significantly improved the quality of life and the symptoms of IBS.
- Prevents diarrhea: Various studies show that S. Boulardii reduces the incidence of diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms by interfering with the colonization of bacteria.
What are the benefits of Probiotics for the treatment of Yeast overgrowth?
Here are some probiotics effective in treating yeast overgrowth:
- Saccharomyces boulardii: This probiotic is yeast but it prevents yeast infections caused by candida. S. Boulardii inhibits the growth of candida and prevents it from colonizing the digestive tract. Not only that, S. Boulardii restricts the movement of candida to other organs from the GI tract.
- Lactobacillus reuteri: Studies show L. reuteri exhibits antifungal properties against Candida species and almost completely inhibits their growth.
The following are some benefits of probiotics for the treatment of yeast overgrowth:
- Inhibits yeast growth: Lactobacilli, a probiotic normally present in many products, can hinder the growth of yeast and kill Candida. The byproducts of probiotic bacterial growth are responsible for the fungicidal action.
- Restores natural gut flora: Disturbances in the gut microbiota and an increase in harmful bacteria in the GI tract are some of the causes of yeast infection and growth. Probiotics consumption helps to restore and alter the gut microbiota.
- Improves immune system: Probiotics can help regulate immune response, modulates the immune system and immune cells, increases anti-inflammatory factors, and improves intestinal barrier function, thus protecting against infections and their spread.
- Probiotics also help increase the number of lactobacilli after antibiotic treatment thus reducing the possibility of yeast infection and overgrowth.
Is inserting Probiotics for Yeast infection safe?
Inserting vaginal probiotics for the treatment of a yeast infection is safe. There are plenty of commercially available intra-vaginal suppositories containing probiotics or other treatments, which are designed to melt and release the drug after insertion. These are tested for various parameters to establish their safety.
Studies show that the direct application of yogurt containing probiotics for the treatment of yeast infection is also safe and effective.
Are Probiotics with Acidophilus strains useful for treating a Yeast infection?
Acidophilus is a strain of lactobacilli and it can be used in probiotics for treating a yeast infection. A study was conducted to evaluate the antifungal properties of L. Acidophilus. In the laboratory, the researchers found that the probiotic was effective in inhibiting the growth of candida species except for a few strains.
A review of the literature shows that L. Acidophilus prevents adhesion and displaces pathogens, has a bactericidal effect, and modulates immunity. The review concludes that the probiotic is effective against recurring vaginal yeast infections.
L. Acidophilus is present in yogurt, studies show that vaginal application of yogurt containing probiotics increased cure rate and improved symptoms of yeast infection.
Is taking Probiotics with Antibiotics effective to prevent a Yeast infection?
Taking probiotics with antibiotics may not be useful to prevent a yeast infection. Antibiotic treatment can affect gut flora and reduce the number of beneficial bacteria such as lactobacilli which may result in yeast infection. A probiotic treatment can restore gut flora and increase the number of lactobacilli. However, concurrent consumption of antibiotics can also render the bacteria in probiotics useless.
A case study suggests taking probiotics along with antibiotic treatment to prevent side effects such as diarrhea, but it may not prevent all the after-effects of antibiotic treatment. A study was conducted to assess the effectiveness of taking probiotics after an antibiotic treatment to prevent fungal infections. The study did not yield positive results concluding the ineffectiveness of probiotics to prevent yeast infection after antibiotic treatment.
What is the relationship between Probiotics and Yeast allergy?
There is an adverse relationship between yeast-based probiotics such as S. Boulardii and yeast allergy, as yeast-based probiotics can worsen a yeast allergy. However, people who are allergic to yeast can take bacteria-based probiotics such as Lactobacilli or Bifidobacterium.
An unexpected allergic reaction can occur after consuming yeast-based probiotics if the person is allergic to yeast, a case report documented the findings when a child had to be admitted to the hospital after consuming probiotic-containing S. Boulardii which is a yeast. The allergy was confirmed after a skin test. Thus it is important to check the ingredients of probiotics to make sure it does not contain any yeast if you are allergic to them.
How long does it take for Probiotics to work for Yeast infection?
The time it takes for probiotics to work for yeast infections depends on the mode of application and the form of probiotics.
- Direct vaginal application: Studies show that it takes about 4 weeks for yogurt containing probiotics to provide relief from the symptoms of yeast infection after vaginal application.
- Oral probiotics: It takes about 1-4 weeks for oral probiotics to treat yeast infections.
- Probiotic vaginal tablets: Studies show that vaginal tablets containing two different strains of probiotics significantly decreased candida symptoms after 28 days of application. After continuing the treatment for one more month only 3 women out of 30 reported recurrence, indicating the long-term effectiveness of the therapy.
What is the dosage of Probiotics for Yeast infection?
The dosage of probiotics varies depending on the form of administration.
- Oral: Probiotics can be consumed orally in the form of capsules. The usual dose of commercially available products is 1-2 capsules per day.
- Vaginal suppository: One suppository per day or as directed by the manufacturer.
- Vaginal tablet: Once a day for the first 7 days, followed by 1 tablet every 3 days for 3 weeks and then 1 tablet every week.
The regulatory agencies have not recommended any standard dose of probiotics for the treatment of yeast infection. Consult your physician or refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for the exact dose.
Can Probiotics cause Yeast to die off?
Probiotic consumption can cause yeast to die off. This is also called the “Herxheimer reaction”. It is a common side effect of consuming probiotics, which causes expedited death of yeast cells. The death of yeast cells releases various toxins, including ethanol and acetaldehyde. These toxins and chemicals cause various symptoms such as:
- Nausea, headache
- Swollen glands
- Bloating, gas, constipation
- Fever, chills
- Weakness
- Skin flushing and rash
- Low blood pressure (mild)
- Increased heart rate
Decreasing the dose of probiotics and drinking plenty of water can help get relief from the symptoms of yeast die-off. Visit your physician if you experience severe symptoms.
The general treatment includes:
- Acetaminophen or fever reducers
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain
- Anti-histamines
Want to know more?
Click the links below to access the individual topic pages:
Sources
This article makes use of information from the U.S. National Library of Medicine under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- Abdelmonem AM, Rasheed SM, Mohamed ASh. Bee-honey and yogurt: a novel mixture for treating patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis during pregnancy. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012 Jul;286(1):109-14. doi: 10.1007/s00404-012-2242-5. Epub 2012 Feb 8. PMID: 22314434.
- Ducluzeau R, Bensaada M. Effet comparé de l’administration unique ou en continu de Saccharomyces boulardii sur l’établissement de diverses souches de Candida dans le tractus digestif de souris gnotoxéniques [Comparative effect of a single or continuous administration of “Saccharomyces boulardii” on the establishment of various strains of “candida” in the digestive tract of gnotobiotic mice]. Ann Microbiol (Paris). 1982 Nov-Dec;133(3):491-501. French. PMID: 6762128.
- Berg R, Bernasconi P, Fowler D, Gautreaux M. Inhibition of Candida albicans translocation from the gastrointestinal tract of mice by oral administration of Saccharomyces boulardii. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1314-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1314. PMID: 8228371.
- García-Collinot G, Madrigal-Santillán EO, Martínez-Bencomo MA, Carranza-Muleiro RA, Jara LJ, Vera-Lastra O, Montes-Cortes DH, Medina G, Cruz-Domínguez MP. Effectiveness of Saccharomyces boulardii and Metronidazole for Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Systemic Sclerosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Apr;65(4):1134-1143. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05830-0. Epub 2019 Sep 23. PMID: 31549334.
- Terciolo C, Dapoigny M, Andre F. Beneficial effects of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 on clinical disorders associated with intestinal barrier disruption. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2019 Feb 11;12:67-82. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S181590. PMID: 30804678; PMCID: PMC6375115.
- Kelesidis T, Pothoulakis C. Efficacy and safety of the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii for the prevention and therapy of gastrointestinal disorders. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2012 Mar;5(2):111-25. doi: 10.1177/1756283X11428502. PMID: 22423260; PMCID: PMC3296087.
- Superti F, De Seta F. Warding Off Recurrent Yeast and Bacterial Vaginal Infections: Lactoferrin and Lactobacilli. Microorganisms. 2020 Jan 17;8(1):130. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8010130. PMID: 31963487; PMCID: PMC7023241.
- Kartal O, Demirel F, Baysan A, Gulec M, Yesillik S, Uyanýk M, Musabak U, Sener O. An unexpected allergic reaction with Saccharomyces boulardii: a case report. Clin Transl Allergy. 2014 Jul 18;4(Suppl 3):P100. doi: 10.1186/2045-7022-4-S3-P100. PMCID: PMC4127795.
- Vicariotto F, Del Piano M, Mogna L, Mogna G. Effectiveness of the association of 2 probiotic strains formulated in a slow release vaginal product, in women affected by vulvovaginal candidiasis: a pilot study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012 Oct;46 Suppl:S73-80. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3182684d71. PMID: 22955364.